GEOGRAPHY OF POLAND AND UKRAINE BORDERLANDS
Extensive article
- No comments
- Read: 11,107
NieznanaUkraina.pl / Articles, Geography / GEOGRAPHY OF POLAND AND UKRAINE BORDERLANDS
 SUMMARY
SUMMARY
The area of Polish-Ukrainian borderlands area takes a special place in the geological structure of the European continent. Are confronted here with each other three major tectonic units of Europe: Precambrian East European Platform, young Paleozoic platform of Western and Central Europe and zone of alpine folds of southern Europe, from a very well developed premountain cavity. 
If you are looking for something similar, check RELATED ENTRIES at the end of this article.
CATEGORY OF ARTICLE: Articles, Geography January 10, 2011, 23:22
The area of Polish-Ukrainian borderlands area takes a special place in the geological structure of the European continent.
GEOLOGY

Precambrian East European Platform, lying east of the zone TT, characterized by a typical two-storey building platforms. The lower floor is the foundation of a crystalline, constructed from the consolidated igneous and metamorphic. Foundation crystalline surface is inclined substantially from the north-east to south-west. Upper floor, units are run, who participated in the foundation of the crystalline structure and the platform cover rocks and Cambrian age późnoproterozoicznego-Carboniferous. For all units are Permian-Mesozoic sediments, whose thickness increases from NE to SW. On the border of Precambrian East European Platform and platform Paleozoic basin lies nadbużańska, where ground faults occur TT border zone.
- Geography of Polish and Ukrainian border 24
- Geography of Polish and Ukrainian border 25
- Geography of Polish and Ukrainian border 27
Paleozoic platform of western and central Europe, occupies almost half of Polish territory and a small patch of the surface in western Ukraine. For the most part is covered with quaternary sediments, mainly of glacial and river. Long-term and complex evolution of the substrate platformer and its sedimentary cover has led to the emergence within it of individuals of various ages.
- Geography of Polish and Ukrainian border 1
- Geography of Polish and Ukrainian border 2
- Geography of Polish and Ukrainian border 3
Carpathian Mountains are the northernmost mountain range in Europe the Alpine folded zone. Their emergence is associated with the collision of the Apulian plate and the liquidation of the European plate oceanic crust in the northern part of the Tethys Sea. They consist mainly of Mesozoic and Cenozoic sedimentary rocks. Smaller role played by lying beneath Paleozoic metamorphic rocks and deep-sea volcanic rocks and Tertiary. The whole system of the Carpathian Mountains are divided into units stretching along a chain and blocks dividing the arc into sections with different construction. Along the arc of the Carpathians Carpathians distinguished internal and external.
- Geography of Polish and Ukrainian border 6
- Geography of Polish and Ukrainian border 9
- Geography of Polish and Ukrainian border 10
Zapadlisko przedkarpackie, ditch which przedgórskim, formed at the front gives rise to the north of the Carpathians, is one of the youngest units of the Alps in Europe. Its emergence is associated with the last stages of the Carpathians tektogenezy. Structural Features, sedimentological and stratigraphic distribution allow Foredeep the inner and outer parts (inside or outside the Carpathian overthrust), and on the part of the western and eastern. Foredeep is filled with sedimentary materials of different origins and thickness Lithologically (until 3500 m). This reflects the highly variable conditions of sedimentation. Foredeep sediments formed in the middle of the pool called Paratethys, that stretched in the Miocene in the northern and eastern parts of today's European and North alpidów foreland.
- Geography of Polish and Ukrainian border 13
- Geography of Polish and Ukrainian border 11
- Geography of Polish and Ukrainian border 14
The entire area in question, apart from the Carpathians has zlodowaceniom Pleistocene. In the Quaternary climate underwent significant changes. By the end of the Tertiary in Europe began to spread tundrowa zone. Next cooling occurred in the Quaternary, which led to continental glaciation in the mid-latitudes. Repeatedly followed by periods of development of ice sheets, przeplatane okresami całkowitego I zaniku. The range of individual glaciations was different. Reached farthest into the foothills of the Carpathians (in Poland) and Lowland Naddnieprzańskiej (in Ukraine). After the withdrawal of the remaining glacier in the area numerous pieces of varying thickness glacial. The sediment is dominated mostly river and lake sediments. Among them, there are considerable deposits of clay, sands and clays.
The formation SURFACE AREA
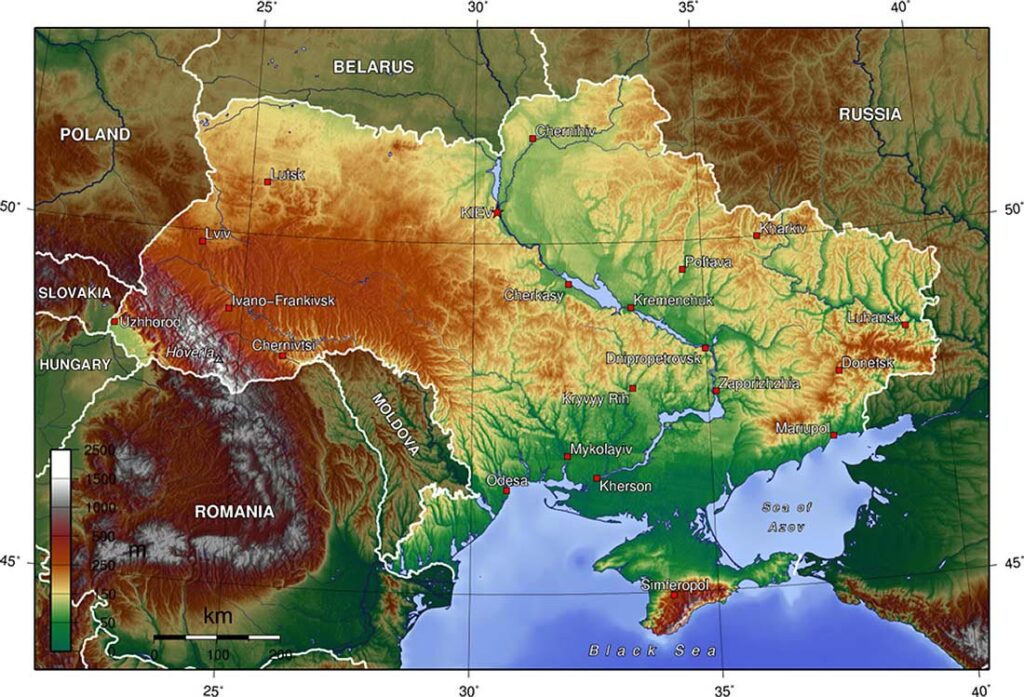
In terms of terrain, area in question can be considered crimson, starting from the north.
The northern part of the border include Eastern European Than, namely the area of Western Polesie and Volhynia Polesie. Polesie is a vast flat plain, which lies within the territory of Belarus, Polish and Ukraine in the basin of the Pripyat and the Bug. Height above sea level in this area varies between 100-250 mnpm. In this area there are many forms of glacial. This is an area rich in lakes, the Polish side of the West Polesie Lakeland is located Łęczna-Włodawskie, while the Ukrainian side in the Polesie Volyn Lakeland Szacki.
From the south Polesie is limited belt heights. The eastern part of the belt includes Volyn Upland, which, together with forms a vast plateau Podolsk Volyn-Podolsk Upland. It is an extensive unit of physio drawn from Polish-Ukrainian border to Upland Naddnieprzańskiej. Volyn Upland, is slightly hilly area in Western Ukraine. It lies in the circuits of Volhynia and rówieńskiego. The belt stretches between the rivers Bug and Lucas. Its width varies from 40 until 50 km. The average height is about 220-250 mnpm, the highlight is the Myżoczskyj Kriaż, whose height is 341 mnpm.
- Geography of Polish and Ukrainian border 15
- Geography of Polish and Ukrainian border 16
- Geography of Polish and Ukrainian border 18
Covers the western part of the Lublin Upland, which in terms of construction and the origin belongs to Central Europe Pozaalpejskiej. Is limited by the valleys of the rivers Bug (east) and the Vistula (West). Almost all of the Highlands is located within the province of Lublin and only a small part of it is in the Małopolska Region. The highlight of the heights are Grabowiecki Departments 314 m npm.
In the south of Lublin Upland and Volyn are limited belt Mites. Mites is a geographical area with a total length 180 km and a width of 12 until 32 km. It is characteristically wypiętrzonym shaft, separating the Lublin Upland and Volhynian from Sandomierz Basin and Transnistria. Belt extends from Krasnik Poland to Lviv in Ukraine. Mites are divided into Western, Mites Mites Central and Eastern. Highest elevation reached 414 mnpm.
Sandomierz Basin is an area of macro-fizycznogeograficznym 15 k. km ², stretching between the North Podkarpackie to the south and the north Roztocze. Its extension in Ukraine is narrow Dnestr Basin. It is a large tectonic zapadliskiem in triangular, filled with sediment mioceńskim. Lies entirely in the Vistula basin.
To the south of the Sandomierz Valley stretches a wide belt of North Podkarpacie, geologically belongs to the Western Carpathians and lies within the Czech Republic, Polish and Ukrainian part. This is a reduction in the assumption of varying widths tectonic. Filled with various marine Miocene sediments. Dehydrate it right tributaries of the Vistula: San, Wisłok, Wisłok, Raba and Dunajec.
- Geography of Polish and Ukrainian border 30 (e)
- Geography of Polish and Ukrainian border 32 (e)
- Geography of Polish and Ukrainian border 40 (e)
Eastern Podkarpacie podprowincją physio is located in Ukraine and partially covers the areas of Polish and Romanian. Geologically belongs to the Eastern Carpathians of Eastern Podkarpacie. Represents foothills of the Eastern Carpathians. Hand and the streams flowing from the Carpathians porozcinały surfaces of the area into several broad plateaus. One of the larger units in the area fizycznogeograficznych is Sańsko Plateau-Dniestrzański. Through its surfaces is Balto-Black Sea watershed, separating the basin of San and Dniester. The plateau is divided into Chyrowski and Krukienicką Upland Plateau. The first determines the farthest extent of Pleistocene glaciation in South Poland.
Further south, the Carpathian bow extends. In the Ukrainian part of the Beskydy mountains are East and Inner Eastern Carpathians. In this area of the Carpathian arc bend to the south towards Romania and take the south-east direction. On the Polish side of the border also includes the Eastern Beskydy. Carpathian Mountains Carpathian lowlands separate, which is the northeastern stretch Of cold air masses from Pannonian coming from the North, creating a microclimate similar to the Hungarian.
CLIMATE
Poland and Ukraine are located in the temperate climate zone, just south shore of the peninsula of Crimea is a subtropical climate zone (Mediterranean). From west to east continental climate increases and decreases the influence of humid air masses coming from the Atlantic. In the southern part of the Carpathian arc of the area creates a barrier to warm air masses coming from the Pannonian Plain and the western part of the circuit only Transcarpathian is in the impact zone of the masses. This results in Ukraine Transcarpathian (Transcarpathia) is very well developed viticulture and wine production, the scale of the rock as in Tokaj and Eger in Hungary. Similarly, in North Podkarpacie Doly Jasielsko-Sanok thanks to its location in a basin formed a distinctive mild microclimate, which promotes the cultivation of vines on slopes with southern exposure.
In Transcarpathia climate is moderate-continental. In the lowland part of Transcarpathia 130 mnpm. average January temperature is -3.1 ° С, July 20.1 ° С. Precipitation is about 770 mm. In the mountainous and highland climate changes with altitude. At the height of 700 mnpm. average temperature change, in January are -7.7 ° С, in July 16.9 ° С, and precipitation 1 030 mm.
In the External and Internal Eastern Carpathians mountain climates, characterized by higher rainfall (more than 1500 mm) and lower average temperatures: -8° C in January and 9th ° C in July (alpine areas).
Livescore.com East in Lviv region average annual temperature is-5 ° c in January and +12 ° C in July. Precipitation varies between 750-1000 mm and their number increases towards the south-west, reaching climaxes on the slopes of the Eastern Carpathians External.
- Geography of Polish and Ukrainian border 41 (e)
- Geography of Polish and Ukrainian border 12 1
- Geography of Polish and Ukrainian border 34 (e)
Podkarpacie has a milder climate of the North. An example can be mild microclimate Jasło-Sanok. The Podkarpackie, can be divided into several sub-climatic: mountain (Carpathians), podgórską (Foothills) in nizinną (Sandomierz Basin). The average temperature in this area are -5 ° C in January and 18 ° in July. There are often long and hot summers, only part of the mountain there are cold winters. Total rainfall varies, from 600 mm in the Sandomierz Basin to 1200 mm in the Bieszczady.
Lublin and Volhynia have similar climatic conditions. The average January temperature is -4 ° C, July +17 ° C. The amount of rainfall varies between 560-620 mm and falls in a south-easterly.
Throughout this area, omitting part of the Carpathians, Transcarpathia and, wind conditions are very similar. The winds vary seasonally, in winter, westerly winds prevail here, bringing together large amounts of moisture. While summer winds are coming from the north-west.
WATER
Ukrainian and Polish territories, have different gradients. In Ukraine, the predominant inclination towards the south-east (SE), while in Poland is dominated by slope in a north-westerly (NW), as evidenced by the slope of the tectonic plates, geodetic measurements and directions of major rivers. Frontier zone lies in the watershed area, separating the catchment of the Baltic Sea and Black.
- Geography of Polish and Ukrainian border 19
- Geography of Polish and Ukrainian border 22
- Geography of Polish and Ukrainian border 28 (e)
The most important rivers, the Polish-Ukrainian border region include: San, Bug, Tanew, Hog, Krzna and Lubaczówka (Baltic Sea basin), and Pripyat, Dniestr, Stryy, Uzh, Latorica (Black Sea basin).
On two odcinakach San River (ukr. Xiang) and Bug (ukr. Western Bug), belonging to the Baltic Sea catchment, form the border between Poland and Ukraine. San River forms its upper reaches in 55 km border belt, starting from the slopes Piniaszkowego (950 mnpm) in the Western Bieszczady meanders around the great circle Smolnik Łysani on the San. Bug River has its source in a village near Zlotshev Werchobuż Upland Podolska Ukraine. In the section 363 km (Pigeons - Niemirow) forms the border with Ukraine and Belarus.
Numerous lakes, consists of two lake districts, lying on similar latitudes and having a similar Genesis creation. On the Ukrainian side, the Lake District which is separated Szacki valley of the Bug River from Lake Łęczyńsko-Włodawskie, lying on the Polish side. Belong to the catchment of different seas, according to the catchment of the Black Sea and the Baltic.
- Geography of Polish and Ukrainian border 29 (e)
- Geography of Polish and Ukrainian border 31 (e)
- Geography of Polish and Ukrainian border 38 (e)
Shatsky Lakes (ukr. Шацькі озера), consists of 30 lakes and is located between rivers Bug and Prypyat among forests in the Shatsk region (Volyn Oblast). For strict protection of rare natural complexes was established in 1983 year Shatsky National Park (ukr. Шацький національний природний парк) area 32 500 ha. Lakeland is the outwash plain of Polissya lowland (Polissya Volhynia), and its lakes are located in large lake bowls. Most of the lakes were created in chalk board during the Pleistocene. There are also lakes, which arose as a result of accumulation and increase of alluvia of ground water, for which favored the low slope in the absence of permanent surface runoff. The edges of the lakes are covered with fine material and gravel sand, sometimes there are marshy areas. The bottom is usually covered with sand and mud material or peat. Supplies are exclusively due to atmospheric precipitation and by groundwater, often using the exchange channels, which connect the lakes in one system. Mineralization of water is moderate or low and varies in the intervals 75 – 125 and 200 – 250 mg / l. The largest lake is Lake of the Lake District Świtaź (ukr. Світязь) area 26 – 27,5 km ², which is the second largest natural reservoir of Ukraine after Lake Yalpug (ukr. Ялпуг), whose area is 149 km ². Another larger lakes of Shatsky lakeland are: Pulemetske (ukr. Пулемецьке)-16,3 km ², Luky (ukr. Луки)-6,8 km ², Lyutsimir (ukr. Люцимир)-4,3 km ², Ostrov'yanske (ukr. Остров’янське)-2,5 km ², Pіsochne (ukr. Пісочне)-1,86 km ² and Krymne (ukr. Кримне)-1,44 km ². In the twentieth century, it was decided to connect by canal Lake Svityaz with the river Prypyat, which resulted in a connection of water of the Baltic Sea with the Black. Etymologically, according to the topographical dictionary of the Ukrainian language word "shacky" comes from the word "oshatnist", which can be translated as "beauty".
- Geography of Polish and Ukrainian border 42 (e)
- Geography of Polish and Ukrainian border 43 (e)
- Geography of Polish and Ukrainian border 39 (e)
Lakeland Łęczna-Włodawskie lies on the Polish side of border, in the marshy plains and zatorfionej Łęczna-Włodawskie. The fall of the lake district 68 lakes with a total area 27 km ², of which the largest are: Uściwierz – 2,8 km ², Wytyckie – 2,7 km ², Dratów – 1,1 km ², White circle Wlodawa - 1,1 km ² and White Sosnowickie - 1,5 km ². Next 10 lakes, exceeds the surface 0,5 km ², but among them is the deepest lake with an area of Piaseczno 0,8 sq km and a depth of 38.8 m. Lakeland Lake Łęczna-Włodawskie depressions formed in numerous termokrasowych. At the clays of glacial origin are chalk cliffs. Yielding to form a vast bowl krasowieniu, which over time has been filled with water. For the protection of large areas of these waters are protected. In areas adjacent to the Cow Marshes Polesie National Park was created (4903 ha) with a "Stupid Swamp"(213 ha), also created Sobiborski Landscape Park (100 km ²) and the Lake District Landscape Park Łęczna (109 km ²), comprising a group of the largest lakes in Lakeland. Nowadays, the lake eutrophication are, and the most serious threat is the Lublin Coal Basin. Coal mining generates a cone of depression around the mine, groundwater. Equally dangerous are powyrobiskowe heap containing large amounts of heavy metals.
In the area of the Carpathian and Subcarpathian region there are numerous sources of mineral water of varying mineralogical composition and characterized by various medicinal properties. There appears also a source of thermal water (Transcarpathian (Zakarpatska) Oblast) used in spas and recreational purposes.
COVER Glebowa
Soil cover of Polish-Ukrainian border area is very diverse. There appears to be depending on the substrate and the origins different types of soils with different profiles and fertility.
For Transcarpathian Lowland, as for the Pannonian Plain, soils are characteristic of river origin (alluvial soil) and brown soils, perfectly suitable for orchards and vineyards. In the Eastern Carpathians are brown forest soil, in the highest parts of mountain meadows and alpine skeletal sites. At Podkarpacie East, Like the North Podkarpacie, soils predominate in turf-podzol, szaroziemy. Forest areas are mostly brown soils and forest chernozem Polesie. Volyn-Podolsk Upland mostly cover chernozem, bielicoziemy and boggy soil. In areas of lakes and Łęczna-Włodawaskiego Szacki, arisen as a result of excessive moisture and soil peat bog soil. And along the major waterways have developed alluvial.
- Geography of Polish and Ukrainian border 4
- Geography of Polish and Ukrainian border 5
- Geography of Polish and Ukrainian border 7
Most suitable for agriculture are chernozem. In comparison with Ukraine, where are the dominant type of chernozem soils (about 60% surface state and 40% global resources), Poland has a small tracts of land, chernozem which (together 1% State space). They are on the Polish-Ukrainian, on board the loess, mainly on the Lublin Upland (lobe Hrubieszów) Kielce-Sandomierz and (lobe Sandomierz), Also at Przemysl foothills (lobe of Przemysl).
COAT PLANT
In terms of geobotanicznym studied area lies within your Holarktyki (Holarktydy), which occupies the largest area of the globe. Within its borders is part of the globe from the North Pole to the Tropic of Cancer. Flora in the area is represented by a family: wierzbowatych, brzozowatych, klonowatych, różowatych, krzyżowatych, skalnicowatych, jaskrowatych and selerowatych. There are numerous grass and species of the family Asteraceae and legumes.
- Geography of Polish and Ukrainian border 21
- Geography of Polish and Ukrainian border 37 (e)
The areas lying on both sides of the Polish-Ukrainian border have common characteristics and are in some way mixed. There are no natural boundaries to the west and the east allows the movement of plant species. In this way, of Upland Volyn-Podolska the loess areas of the Lublin Upland and the surrounding Przemysl, steppe vegetation arrived, belongs to the Province of Pontic-Pannonian (Tarsometatarsal Forest Department). In a similar way to the Carpathian arc moving plants belonging to the province of the Carpathian (Department of East and West Carpathians). Most of the land contained within the European Area of deciduous and mixed forests.
ŚWIAT ZWIERZĘCY
In terms of zoogeograficznym entire area in question lies in the realm of Palaearctic, that coverage includes Europe, North Africa and almost the whole of Asia, the Tropic of Cancer. Animals found in this region is characteristic of temperate, and in the Carpathians - a mountain.
Many endangered species of animals live in nature reserves and national parks. They are under strict state protection, For example, a unique type tarpan Polish pony living Roztocze National Park and numerous waterfowl inhabiting areas of lakes and Łęczyńsko-Włodawskie Szacki. Formed in 1992 , the International Biosphere Reserve “Eastern Carpathians”, includes 3 Polish national parks, Ukraine and Slovakia. It is a unique biome with the characteristic animal world and the vegetation.
ARTICLE TAGS
 COMMENTS TO THE ARTICLE
COMMENTS TO THE ARTICLE
YOU CAN LEAVE THE FIRST COMMENT
AND START INTERESTING DISCUSSION
About Site
NieznanaUkraina.pl
happy reading about Ukraine, We encourage you to actively comment! About page
 Comments
Comments
- Małgorzata wrote in BALNEOLOGICAL RESORT NEMYRIV :
My great, great, great grandfather was born in Niemirów in... 1865 y. His mother's family ( Lechańska Rozalia) from there… - Valentina wrote in KREMENETS : HOME TOWN OF JULIUSZ SŁOWACKI :
Hi, how can I get information about the towns in Kremenets by 1920th? I want to know about m'y roots.… - Pan Prozak wrote in SAMBOR :
So. It used to be a beautiful city! Well, what did they do to the Falcon's house during the Soviet era?… - Wojciech Zaleszczak wrote in FREDROWSKIE RUDKI AND BEŃKOWA WISZNIA :
My grandfather, Adam Zaleszczak, born in 1919, came from Rudki Fredrowskie. Maybe someone something? - tacjanna wrote in UNKNOWN VILLAGE MAIDAN :
The books are in the Archdiocesan Archives in Przemyśl, but difficult to access. However, there are scans of Greek Catholic records available on the Internet… - Anna B wrote in UNKNOWN VILLAGE MAIDAN :
Hello Marcin, my Grandma Helena née Pachla, had a sister, Karolina, and they lived in the village with my grandfather, Kazimierz Koziol… - Ew wrote in MAIDAN : THE LAND OF ANCESTORS :
Hello, my grandmother's name was Józefa Pasiniewicz (from home important) in Poland they settled with their grandfather Stanisław Pasiniewicz first…
SEARCH
ON WEBSITE
INFORMATIONS
POPULAR
Articles, that read the most timesWHAT CAN BE TRANSPORTED BY ... : 167,711
UKRAINIAN LARD: SAŁO.. : 83,808
UKRAINIAN CIGARETTES AND YOU .... : 80,137
NATIONAL SYMBOLS OF UKRAINE : 63,916
BY TRAIN VIA UKRAINE: ... : 62,690
UKRAINIAN LANGUAGE and ALPHABET : 58,865
POLAND - UKRAINE BORDER : 47,326
THE PURCHASE OF RAILWAY TICKETS ... : 42,202
EXCHANGING CURRENCY IN UKRAINE : 42,131
BEFORE YOU TRAVEL : 34,337
MOBILE IN THE UK.. : 33,608
HOLIDAYS IN UKRAINE : 33,489
A TRIP THROUGH MEDYKA : 1ST... : 32,094
FAMOUS UKRAINIANS : 31,591
CRIMEA : AUTONOMOUS REPUB .... : 30,227








































 CASTLES OF THE WESTERN UKRAINE
CASTLES OF THE WESTERN UKRAINE INDEPENDENCE DAY OF UKRAINE
INDEPENDENCE DAY OF UKRAINE NATIONAL ANTHEM OF UKRAINE : TO THE INDEPENDENCE DAY OF UKRAINE
NATIONAL ANTHEM OF UKRAINE : TO THE INDEPENDENCE DAY OF UKRAINE NATIONAL SYMBOLS OF UKRAINE
NATIONAL SYMBOLS OF UKRAINE
Post your comment